CAVITIES
Dr. Chanh Viet
Tooth decay is the destruction of the hard tissue of the teeth like enamel and dentin. It can happen to any age. The bacteria in your mouth form a plaque or a thick layer of bacteria on tooth surface. When you eat or drink foods containing sugars, bacteria in plaque will transform sugar into acids that attack the tooth enamel and dentin; eventually the enamel will break down and form a cavity.
Dental caries (or cavity, or tooth decay) and gum disease are two main diseases that cause missing teeth.
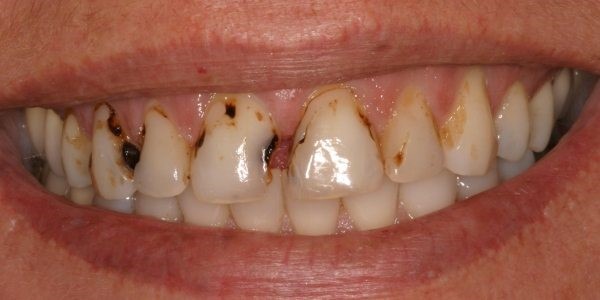
Untreated cavities will spread to the pulp and cause pulpal infection and tooth abscess.
The bacteria in the cavities may penetrate the thin wall of dentin and cause infection of the pulp. Infected pulp can be swollen and cause pressure to the nerve ending inside the pulpal cavity. Toothaches is the pressure to the nerve in a confined space of the pulp chamber.
Over time, all the infected nerve and blood vessels in the pulp will die and become a mass of necrotic tissue overgrown with bacteria. At this time, you may feel a relieve in pain but the infection is not over. The process of forming a tooth abscess is on the way.
Signs and symptom of tooth decay:
- Sensitive to hot, cold, sweet or sour foods.
- You may see the cavity on the tooth.
- Pain when chewing.
- Toothaches, solicited or unsolicited pain.
Types of cavities:
There are different types of cavity. Some types are prevalent in certain group of age. The way to detect, treat and prevent the cavities are also different.
- Chewing surfaces cavity: Those cavities are prevalent in teenagers, it starts at the depth of pits and fissures of the chewing surfaces. The size of the cavity is growing quickly. Pit and fissure sealant is good way to prevent this type of cavity.
- Smooth surface or contacting surface cavities are prevalent after 20s. It starts
at the contacting surfaces between two adjacent teeth where the toothbrush cannot reach. Flossing after meal and fluoride application are good ways to control those cavities.
- Root caries: It happens in older population where gum recession exposes root surfaces. Root decay is difficult to prevent and treat.
- Cavity under the existing fillings or crown and bridges: this cavity is hard to detect. Most of the times, this type of cavities is found during the dental checkup when you have X ray images.
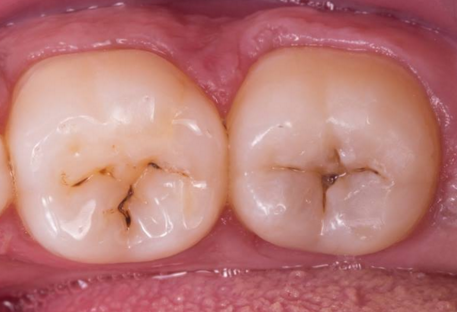
Pit and fissure cavities.
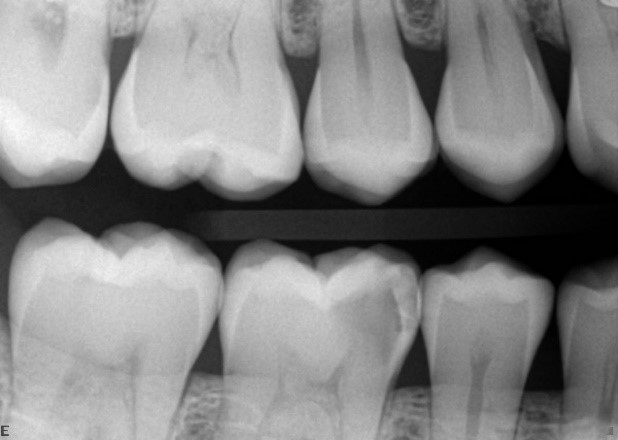
X ray images help to detect contacting surface cavities.
Risk factors:
- Tooth location: Your back teeth have higher risk of caries because those areas are hard to reach during brushing. Pit and fissures of posterior teeth tend to trap food and bacteria that cause tooth decay. Those back teeth also have multi roots, once the gum receded, it tends to trap foods.
- Foods and drinks: Sweet, sticky foods and drinks like cakes, cookies, chips, soda, milk, candies – all are likely to cause cavities because sugar will be converted into acid in the presence of bacteria. Sticky foods cannot be washed away by saliva and cause more harms.
- Frequent snacking or sipping: This habit is harmful to your teeth because the presence of starch, sugar and bacteria in your mouth are key components to produce acid that attacks your teeth.
- Bedtime infant feeding: Milk and juice contain sugar if it remains in the child mouth overnight may cause rampant caries of the baby teeth (cavities on many teeth in the mouth). Constantly sucking baby bottle are also harmful as frequent snacking.
- Dry mouth: This is a condition of lacking saliva. Saliva helps in washing away bacteria and food particles and it also neutralize the acid produced by the bacteria. Lacking of saliva may lead to many cavities in the mouth that are hard to treat. The causes of dry mouth are discussed in depth in the topic “Dry mouth”.
- Ages: Children and elderly people who cannot take care their teeth also have a higher risk of cavity.
- Inadequate or poor oral care: Two minutes brushing, two times a day is really helpful to lower caries risk.
- Acid reflux or heartburn: Individuals who have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), acid from stomach can flow into your mouth and erode the tooth enamel. Without enamel protection, teeth become more vulnerable to decay. Your dentist may find out this problem during periodic exam.
- Not getting enough fluoride: Fluoride help prevent cavities and can reverse the early enamel erosion cause by acid. Fluoride may occur in natural water or added to tap water to prevent cavities; it is also added to tooth paste or mouth rinse. Bottle water may not contain fluoride.
- Host defense: Each individual may have different resistance to tooth decay, some have a lot of cavities in their mouth, the others have less or no cavity at all. This difference can be interpreted as the host defense to bacterial activities in your mouth. Your dentist may have different treatment plan depends on the amount of new cavity in your mouth. You may see your dentist more often and need a more extensive prevention.
Complications:
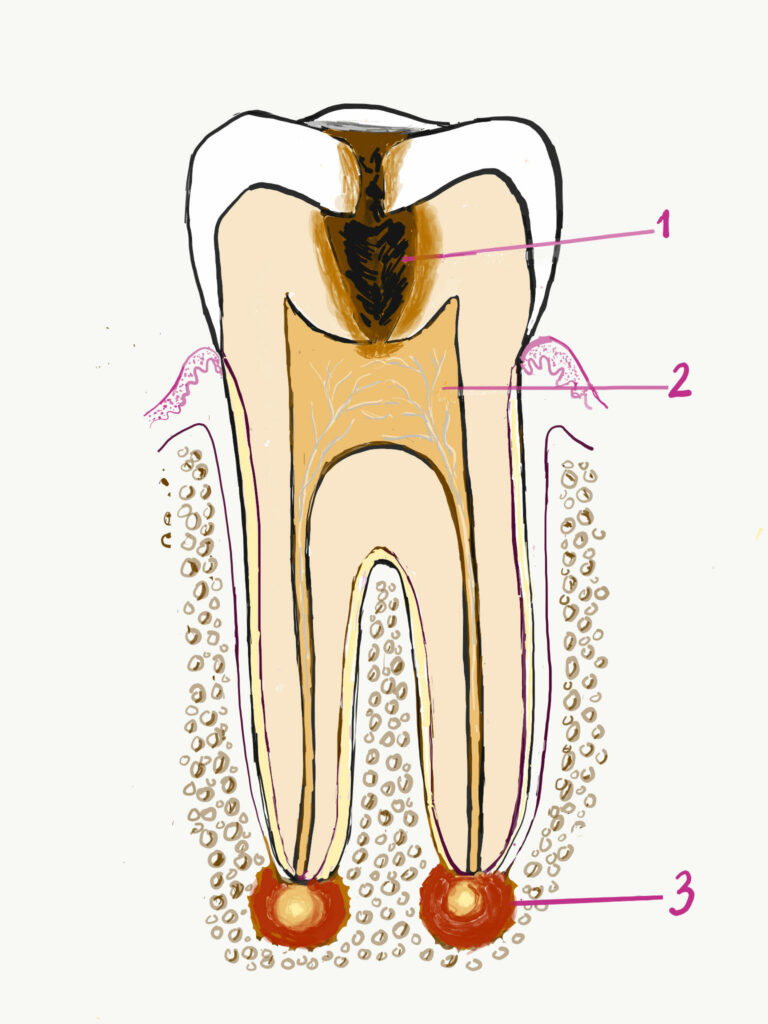
Untreated cavity (1) will cause pulpal infection and necrosis (2) and tooth abscess (3).
Tooth decay is a common disease and many people do not consider for a thorough treatment, especially the treatment of your babies’ teeth. Most of the time, the damages cause by tooth decay are severe and irreversible. The early loss of baby teeth also affects the development of permanent teeth. Common complications of tooth decay are:
- Pain caused by irritation or infection of the pulp.
- Swelling or pus around your teeth.
- Tooth abscess: this complication is discussed in depth in topic “Tooth abscess”.
- Damage or broken tooth leading to tooth loss.
- Lack of chewing efficiency due to pain or missing teeth.
- Shifting of the remaining the teeth that affects the chewing and appearance.
Prevention:
Generally, the key points in cavities prevention are good oral care and good eating habits.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride tooth paste.
- Using dental floss to clean the contact point between your teeth.
- Limit snack times, carbohydrate foods and sugar drinks.
- Eating healthy foods especially fruits and vegetables that contains fibers; the friction of those fibers to your teeth when chewing will keep your teeth cleaned.
- Keep your regular dental visit and ask your dentist of the preventive treatments like fluoride, pit and fissure sealants. People with cavity- high risk may need to see your dentist more often, for example once every three months.
In summary, treating and preventing cavities are the main works each dentist has to do in everyday practice. However, the understanding of the problems cause by tooth decay can help you fighting the disease more effectively.